Syllogism basic concepts
CAT stands for common aptitude test. CAT syllogism is important and useful in logical as well as verbal ability section. An aspirants could except 3 to 4 questions from this topic. As Logical reasoning section contain a total of 20 questions and out of that few questions are from syllogism. A Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation contains 30% weightage in CAT exam.
Questions from this section are frequently asked as per pervious paper analysis. To solve the questions based on Syllogism in CAT, candidates first have to understand the meaning of statements then move for the conclusions and after that mark the answer. With the help of some methods. For example Venn Diagrams and analytical methods. We can solve Syllogism questions. Read the article to know more about some tricks, important formulas, and solved sample questions.
Meaning of syllogism for CAT exam
Syllogism is a Greek synonym of the word conclusion or inference. A more proper definition of syllogism is an argument the conclusion of which is supported by two propositions, of which one contains the term that is predicate of the conclusion, and other contains the term that is subject of the conclusion; common to the both premises is the term that is excluded from the conclusion.
Now, this definition of syllogism seems to be a bit confusing but, as this article proceeds you will one by one understand the deeper meaning of this definition. Before illustrating the example of syllogism. First understand what do you mean on term proposition? A proposition is a sentence that makes a statement and gives a relation between two terms. Each proposition has three parts that forms the sentence structure i.e. subject, predicate and relation between both. Consider these two propositions:
Conclusion: All Rajasthani’s are Kind.
Let’s interpret the conclusion in terms of definition of Syllogism. Now in the sentence, All Rajasthani’s are Kind you can notice that the predicate of the proposition 2 became the predicate of conclusion (the word Kind) and the subject of the proposition 1 became the subject of conclusion (Rajasthani’s) and the common relation between the two (Indians) is missing from it. Thus, this conclusion exactly follows the definition of Syllogism.
Syllogism for CAT Logical Reasoning Formulas
Some rules to solve the problem of Syllogism for CAT Logical Reasoning are as follows.
- All +All=All
- All +No=No
- All +Some=No conclusion
- Some +All=Some
- Some +No= Some Not
- Some +Some= No Conclusion
- No +All = Some Not(Reversed)
- No +Some=Some Not (Reversed)
- No +No=No Conclusion
Ways to determine conclusion of syllogism for CAT exam.
There are two ways to determine that which conclusion will follow.
- The Venn Diagram Method.
- The Analytical Method.
Venn Diagram Method.
Another method of solving such type of questions is by drawing Venn diagram representing the statements. However, it is important that all possible Venn diagrams show as. If a conclusion can be deduced from all the possible solutions then that conclusion is true. If the conclusion can be concluded from one of the possible Venn diagram and not from the other possible Venn diagram then that conclusion is taken as false.
Therefore, Let’s have a look at the table below to understand Syllogism more clearly
Analytical Method.
Following are the four major types of statements generally asked:
| Sr. No. | Type of statement | Represented by the letter | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Universal Positive | A | All boys are handsome |
| 2 | Universal Negative | E | No girl is clever |
| 3 | Particular Positive | I | Some rats are dogs |
| 4 | Particular Negative | O | Some ships are not planes |
While deriving conclusions, following points should be kept in mind:
- With two particular statements, no universal conclusion is possible.
- With two positive statements, no negative conclusion is possible.
- With two negative statements, no positive conclusion is possible.
- With two particular statements, no conclusion is possible, except when an 'I' type of statement is given and then by reversing it, an 'I' type of conclusion is given.
- A statement of type 'E' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'E & O'.
- A statement of type 'A' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I'.
- A statement of type 'I' when reversed, gives a conclusion of type 'I'
- A statement of type 'O' when reversed, does not give a conclusion of any type.
Syllogism for CAT Logical Reasoning Shortcut Tricks
Some steps to convert a solution into the possibility are given below:
- If All A are B, then it can be said – Some B are not A is a Possibility.
- If Some B are not A, then it can be said – All A are B is a possibility.
- If Some A are B, then it can be said – All A are B is a Possibility and All B are A is a Possibility.
- All Some <———> Not Reversed
- Some <———-> All
- NO Conclusion = Any Possibility is true
Some implementations for the solution from a single statement are given below:
Hence, Let’s have a look at the table below to understand Syllogism more clearly
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video’s that could help aspirant.
Solved Examples of Syllogism for CAT
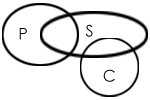
For Example 1:Which of the two conclusions can be concluded on the basis of given statements?- Statements:
- Some parrots are scissors.
- Some scissors are not combs.
- Conclusions:
- Some scissors are parrots.
- Some combs are parrots.
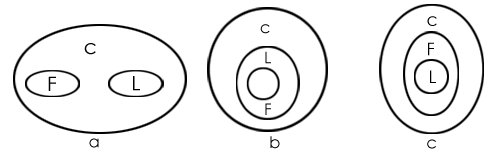
- Statements:
- All flowers are candles.
- All lanterns are candles.
- Conclusions:
- Some flowers are lanterns.
- Some candles are lanterns.
Conclusion I follows from last two possible solutions, but does not follow from the first possible solution. Therefore, this conclusion is false.
Conclusion II follows from all the three possible solutions.
Therefore, conclusion II is true.
- Statements:
- All prisoners are men.
- No man is educated.
- Conclusions:
- All prisoners are uneducated.
- Some men are prisoners.
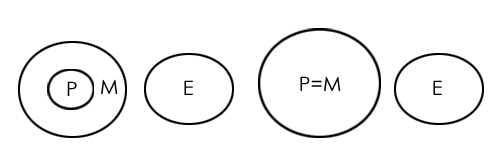
Conclusion II also follows from both the possibilities, so conclusion II is also true.
Therefore, both conclusions are true.
Some question to practice Syllogism for CAT
Question 1 : In the below section, there are four arguments. Four arguments are given. Each argument is a set of three sentences. Select the set that is the third one considered. As the logical solution of both the first and the second one.- All cats are babies. All babies are young. All cats are young.
- Some nerds are fools. Some fools are green. Some nerds are green.
- Cars are well-built. Well-built sustains. Cars sustain.
- All cyclists are fast. Some are fast wrestlers. Some cyclists are wrestlers.
- Only I
- II, III and IV
- I and II
- I and III
- Some A are B. All B are C. Some A are C.
- All men are yellow. No yellow are women. No men are women.
- No ring is a chain. Some chains are watches. Some rings are watches.
- Every P has a Q. All Q are R. No R has a P.
- I and III
- II
- I and II
- III and IV
